Learning Multi-Arm Manipulation Through Collaborative Teleoperation
Albert Tung*1, Josiah Wong*1,Ajay Mandlekar1,Roberto Martín-Martín1,Yuke Zhu2, Li Fei-Fei1, Silvio Savarese1
* These authors contributed equally. 1Stanford Vision and Learning Lab. 2The University of Texas at Austin
To address these challenges:
- We present Multi-Arm Roboturk(MART), a multi-user data collection platform that allows multiple remote users to simultaneously teleoperate a set of robotic arms and collect demonstrations for multi-arm tasks
- We show that learning from such data consequently presents challenges for centralized agents that directly attempt to model all robot actions simultaneously
- We propose and evaluate a base-residual policy framework that allows trained policies to better adapt to the mixed coordination setting common in multi-arm manipulation, and show that a centralized policy augmented with a decentralized residual model outperforms all other models on our set of benchmark tasks.
Paper
[Arxiv]System Diagram
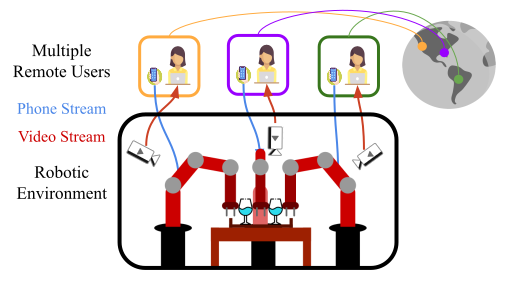
System diagram showing multiple remote users connecting to a single simulated robotic environment.
Example of MART Teleoperation
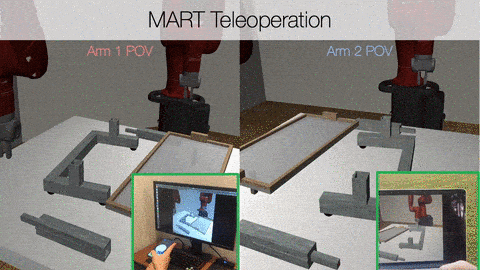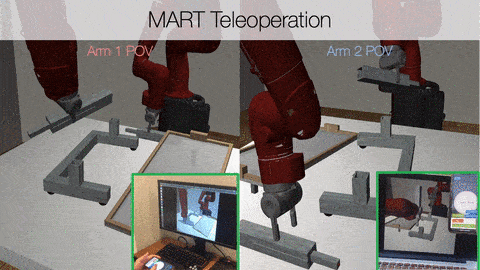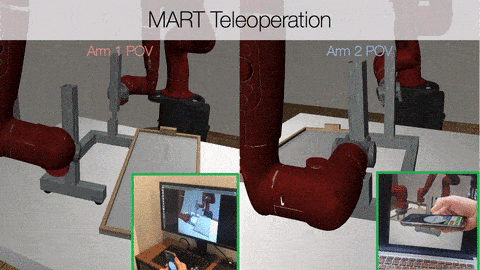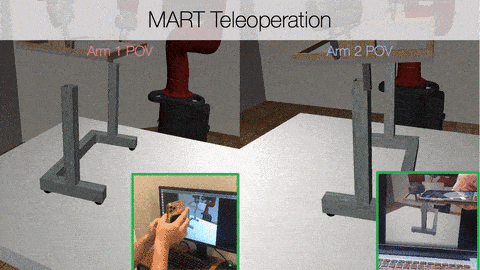
Two users with different points of view controlling robots in a singular environment.
Multi-Arm Tasks
Two-Arm Assembly
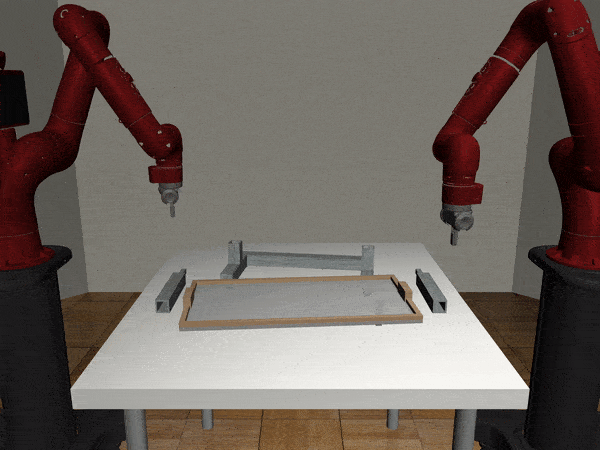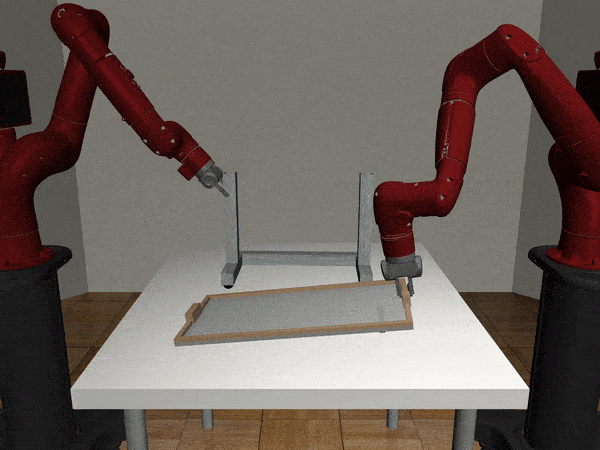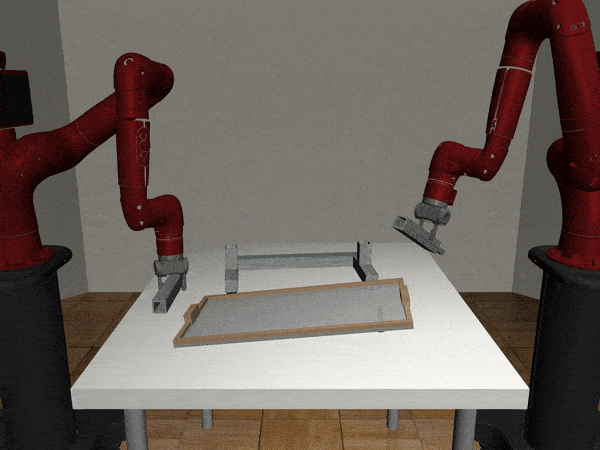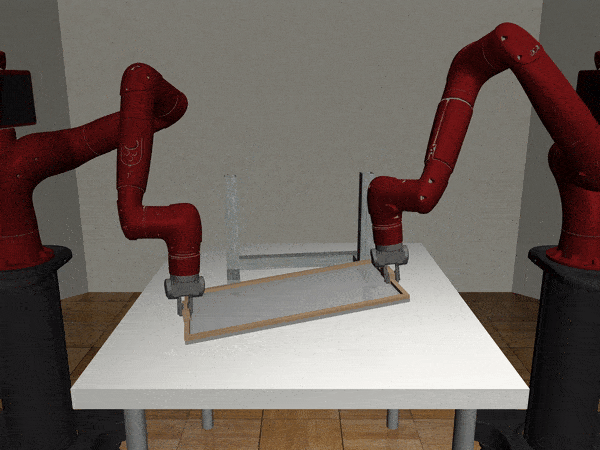
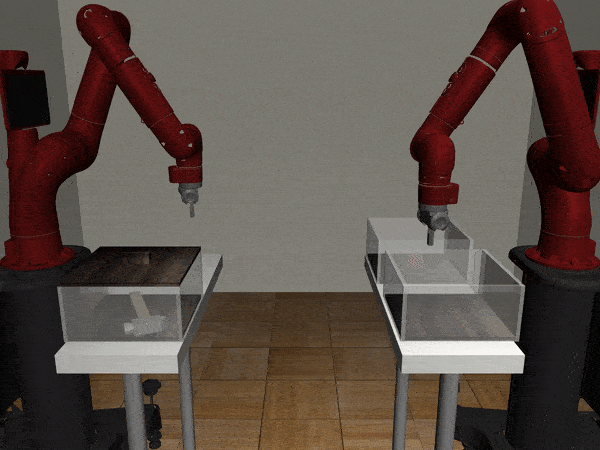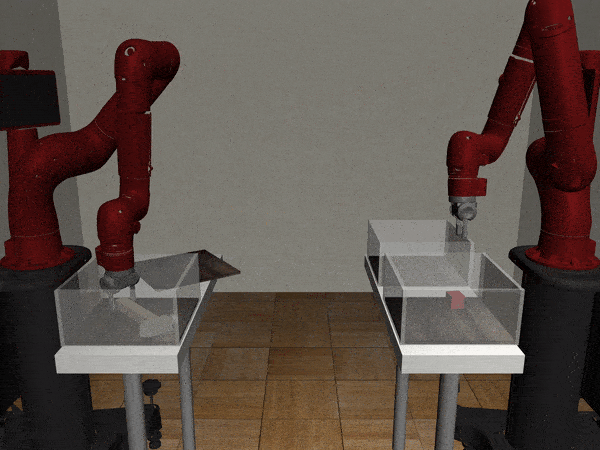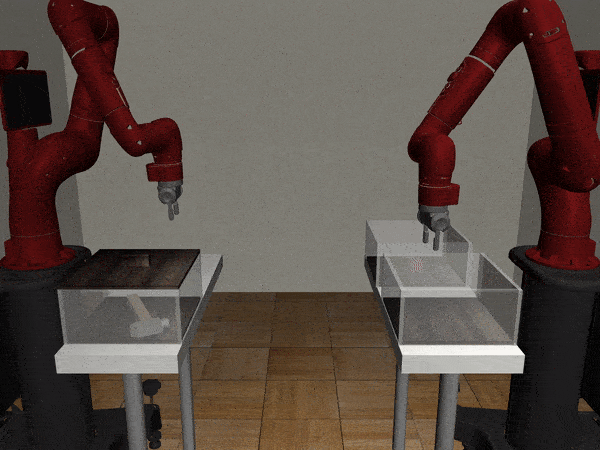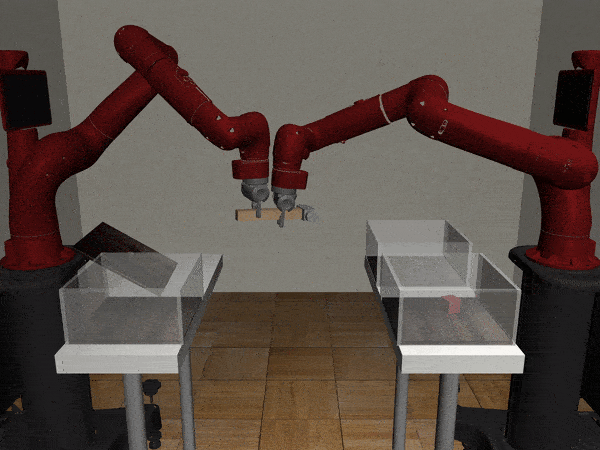
Two-Arm Pick Place Handover
Three-Arm Tray Lift and Wipe
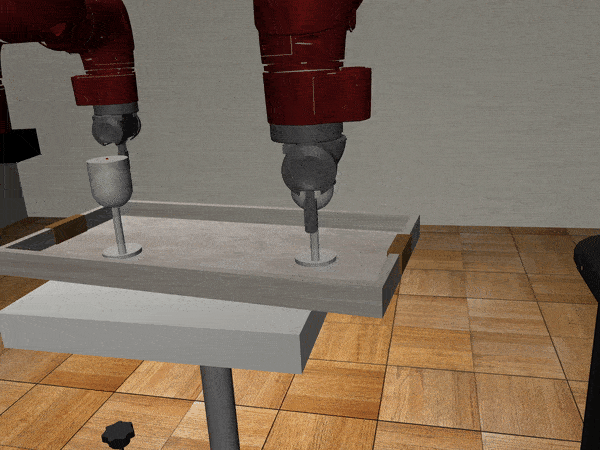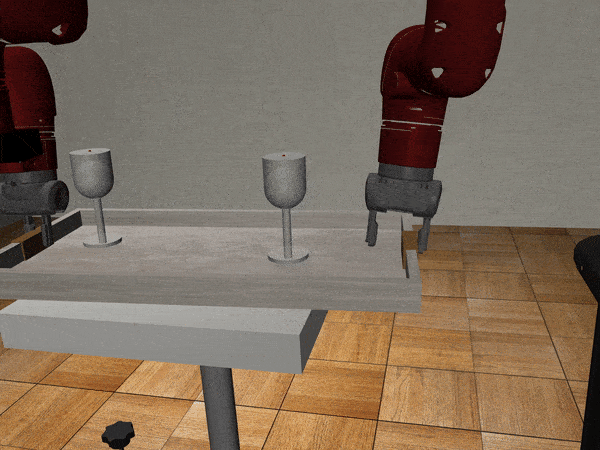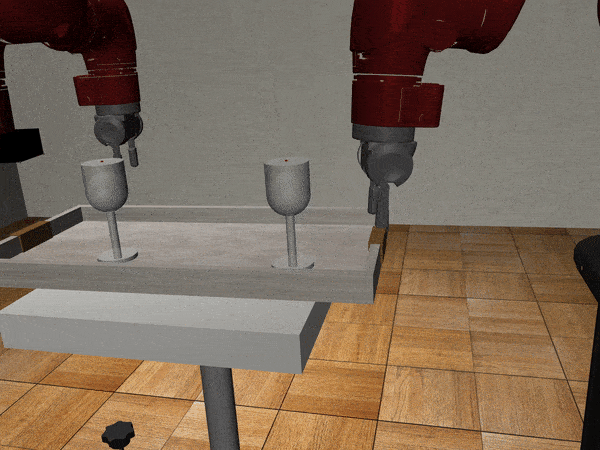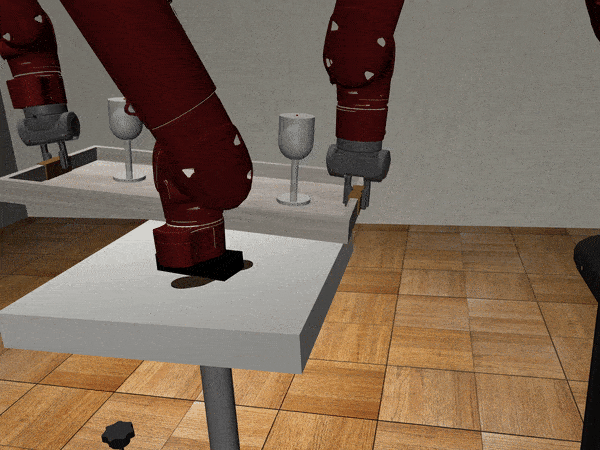
We collect nearly 500 human guided demonstrations using MART
Comparison of Algorithms
Two-Arm Assembly
Centralized
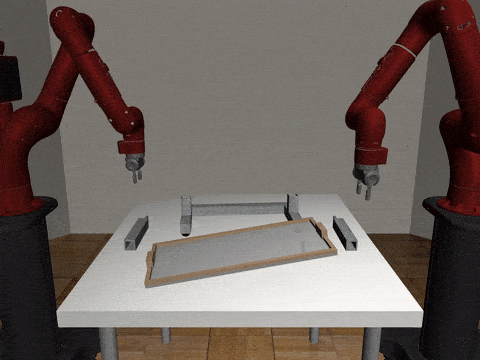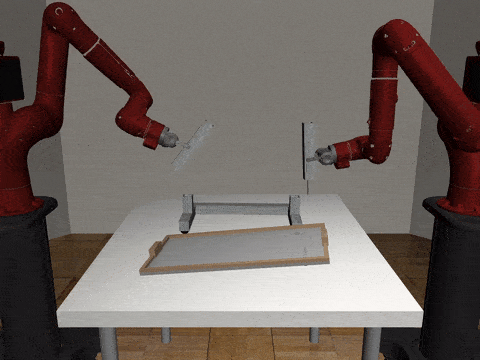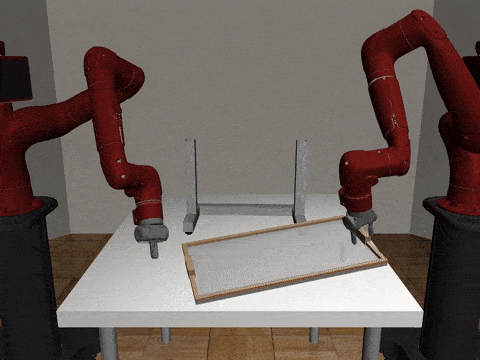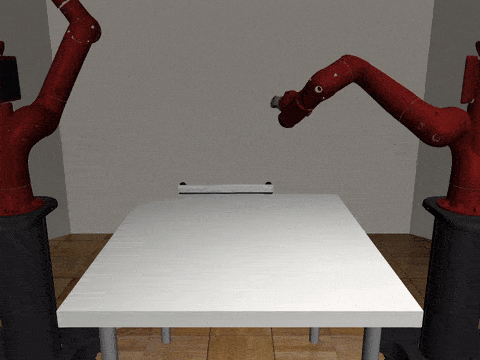
Decentralized
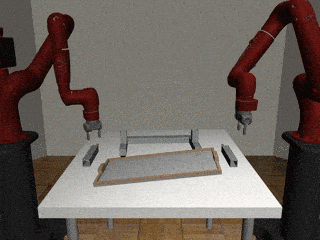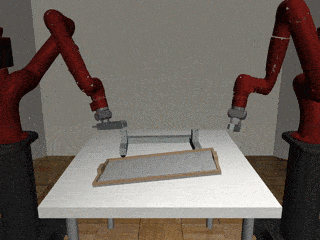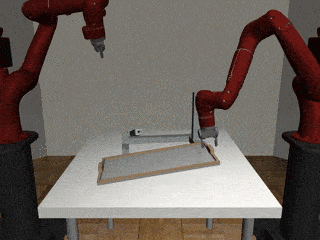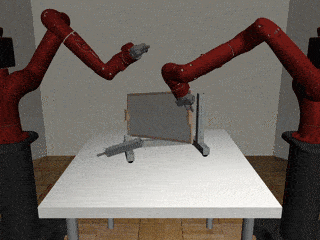
Our Residual Model
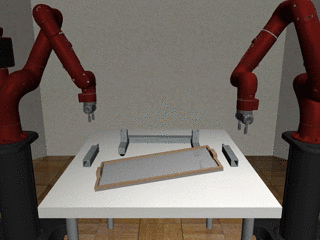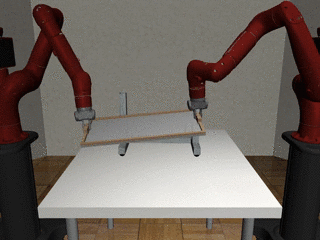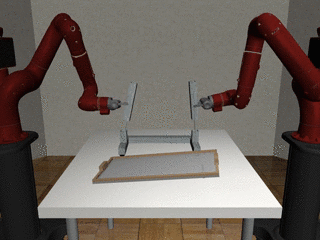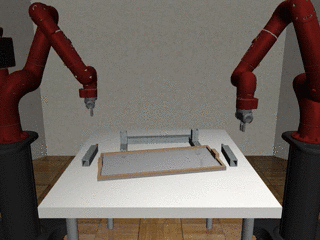
Our residual model is better able to learn decoupled and coupled actions in the assembly task.
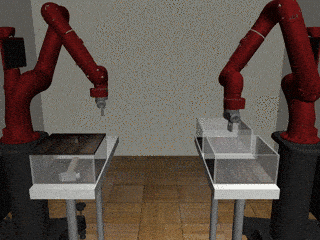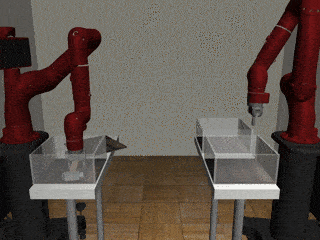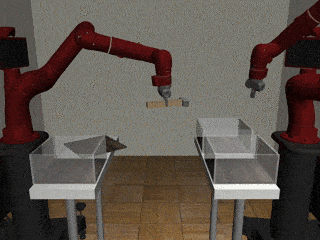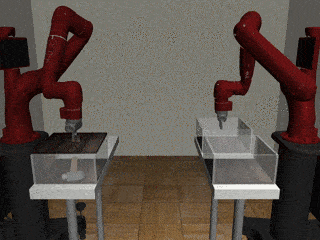
Two-Arm Pick Place Handover
Centralized
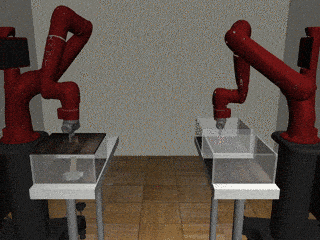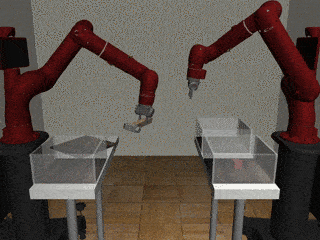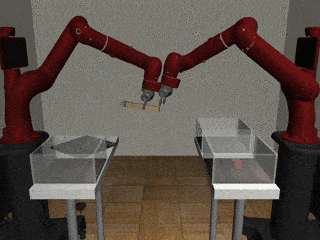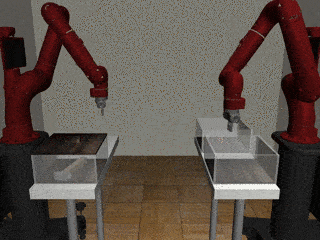
Decentralized
Our Residual Model

Our residual model more often completes the handoff successfully.
Three-Arm Tray Lift and Wipe
Centralized
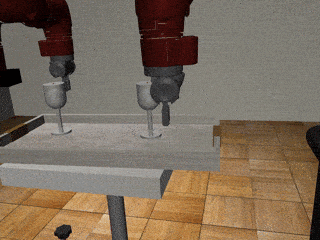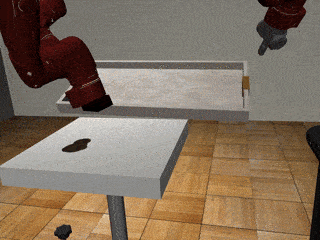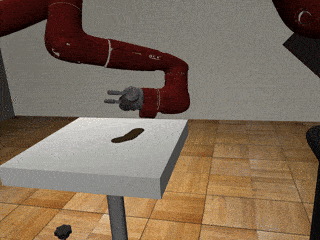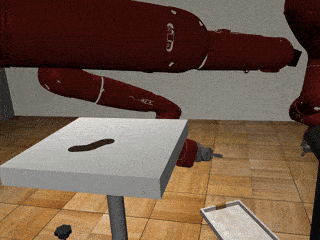
Decentralized
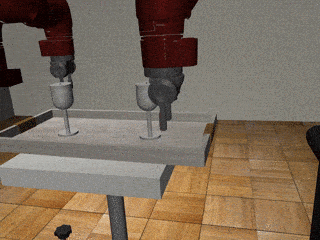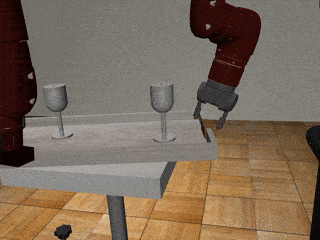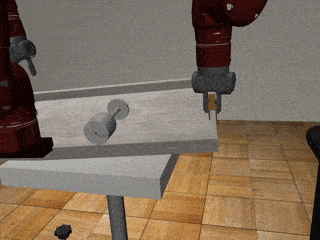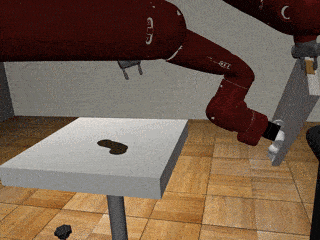
Our Residual Model
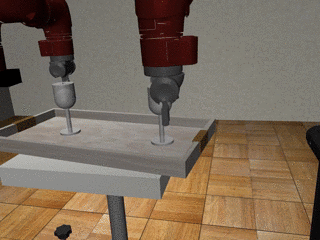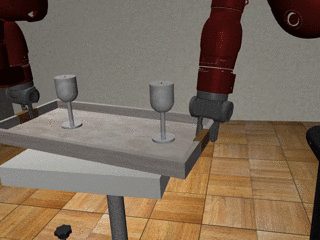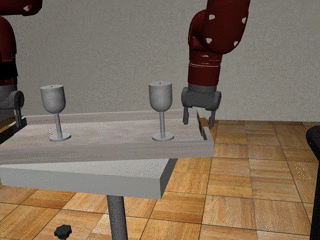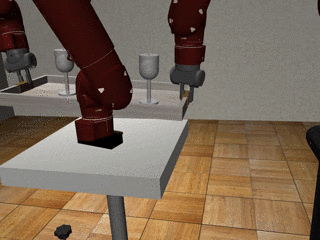
Our residual model recovers from failures more effectively and deals with mixed coordination better.